Leaders of Their Own Learning
A New Beginning
As the 2018/2019 school year approaches, I am embarking on a new journey. I am leaving my former position as a Special Education teacher of 2nd graders. I am moving to a new school and becoming a 3rd grade homeroom teacher. This change has ignited my spirit and eagerness to improve my teaching practices. At my new school, Project Based Learning (PBL) is the norm. This is very new to me and I am having to re-learn how to teach!
As I read and learn more about expeditionary learning and project based learning I am going to post about each step of the journey. I hope this will help other teachers who are new to PBL and need to know how to begin.
My first step in the process is to read Ron Berger's "Leaders of their Own Learning: Transforming Schools Through Student-Engaged Assessment". Ron Berger is the chief academic officer for Expeditionary Learning at Eleducation. This book consists of 8 chapters as seen below:
Introduction:
Learning Targets
Checking for Understanding during Daily lessons
Using Data with Students
Models, Critique, and Descriptive Feedback
Student-Led Conferences
Celebrations of Learning
Passage presentation with Portfolios
Standards-Based Grading
Each chapter describes a stage of Student-Engaged Assessment. Student-engaged assessment is a system of interrelated practices that positions students as leaders of their own learning. The following is a graphic to help understand the flow.
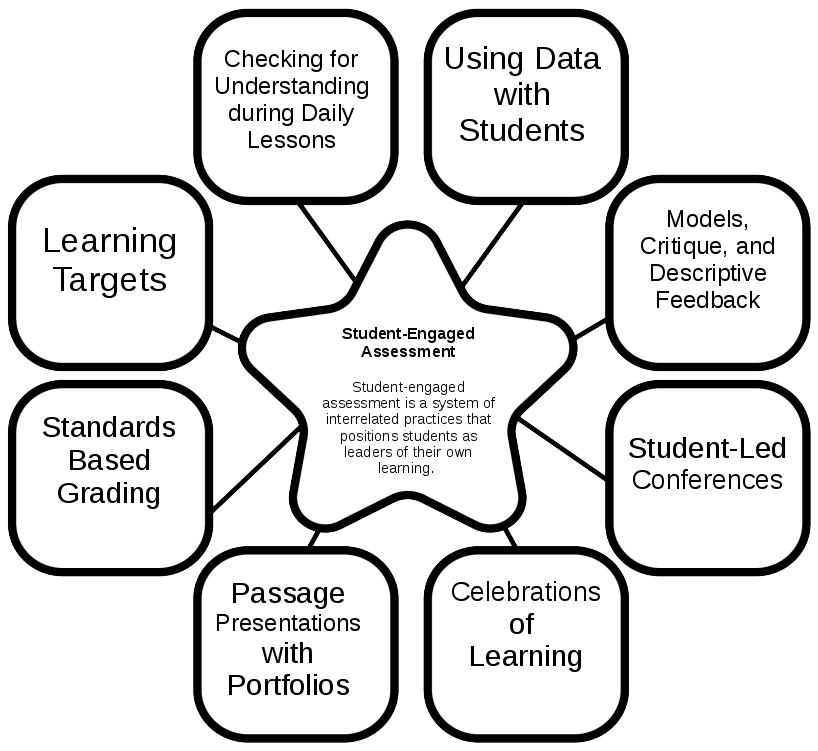
There are many reasons to use this structure. First of all it is very motivating for students. It will have each child taking ownership about their learning and making decisions to better themselves. It will help children (and grown-ups) change their mindset about intelligence. They will go from believing “You are smart because you are born that way.” to “You work hard and put forth effort and you will experience success.” Children will be taught and required to reflect on their learning and abilities. It will help create a culture of trust in your classroom where children respect and collaborate with each other naturally. This process will build the home-school connection by involving parents in the celebration of learning. And finally, it will give students’ a voice to their lives.
Chapter 1: Learning Targets
- Learning targets
Goals for lessons, projects, units, and courses. They are taken from standards and turned into student friendly language ("I can" stems). Learning targets help make learning clear and attainable. They make larger goals manageable and help students experience success.
Getting Started
Writing Learning Targets
Choose a standards-based lesson with which to get started
Write learning targets for the lesson: You need to make learning targets for this lesson focusing on what you want the children to learn, not make or do. Make sure the target is clear and manageable.
Using Learning Targets
Introduce the target at the best point in the lesson
Develop techniques to check for student understanding
hand signals
written checks
verbal check
progress charts
peer check-ins
quick quizzes
"Clicker" technology
In Practice
Long Term Learning Target |
Supporting Learning Targets |
|---|---|
I can overcome learning challenges by being an effective learner: taking initiative and responsibility, preserving and collaborating. |
I can discuss and record what I notice and wonder about resources. |
I can infer the topic of this module from the resources. |
|
I can select a research reading book that I want to read. |
|
I can talk with a small group, using complete sentences to tell why I chose my book. |
Integrating Character Learning Targets
Use your school wide habits of scholarship or character expectations to set clear character learning targets.
Aligning standard, learning targets, and assessments
Considering the rigor of Learning Targets
The 3 types of learning targets are knowledge, skill, and reasoning. Teachers also need to consider the complexity of the students’ task and assessments. Knowing where the task falls on the matrix can inform backward planning, helping teachers ensure that learning targets will scaffold students’ learning. See the Cognitive Rigor Matrix Table
Recall and Reproduction |
Basic Application of Skills and Concepts |
Strategic Thinking and Reasoning |
Extended Thinking |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Remember |
Recall or locate basic facts, details, events. |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
Understand |
Describe or explain who, what, where, when, or how. |
Explain relationships, summarize, identify main ideas. |
Explain, generalize, or connect ideas using supporting evidence. |
Explain how concepts or ideas specifically relate to other content domains. |
Apply |
Use language structure or word relationships to determine meaning. |
Obtain and interpret information using text features. |
Apply a concept in a new context. |
Select or devise an approach among many alternative to research a novel problem. |
Analyze |
Identify whether information is contained in a graph, table, and so on. |
Distinguish between relevant and irrelevant information. |
Analyze interrelationships among concepts, issues, or problems. |
Analyze complex or abstract themes or perspectives. |
Evaluate |
N/A |
N/A |
Justify or critique conclusions drawn. |
Apply understanding in a novel way, with justification. |
Create |
Brainstorm ideas about a topic. |
Generate hypotheses based on observations or prior knowledge. |
Develop a complex model for a given situation. |
Articulate a new voice, new knowledge, or perspective. |
Critical Moves for Deepening Student Engagement
In order for the practice of using learning targets to work, you have to get the students’ to internalize the value of learning targets and use them to assess their progress. Have students analyze and unpack learning targets to get a clear picture of what needs to be accomplished. When teachers use learning targets every day in every class, students will have a strong sense of responsibility and accountability for their learning.
Summary
In this chapter, I learned to create learning targets to help students take ownership of their learning. I need to identify what standards/lessons I need to teach and then create long term learning targets to address those goals. I then need to break down the long term targets into smaller, attainable supporting targets that scaffold up to the long term target. I need to keep in mind and differenciate my targets to incorporate all areas of rigor and levels of thinking. When teaching, I need to make sure students analyze the targets and internalize them. That way students will be motivated to take ownership of their learning and know exactly what is expected of them.
Thank you for reading my review/summary of the book "Leaders of their Own Learning" by Ron Berger.
Check out other chapters by clicking on the links below:
No comments:
Post a Comment